Additive manufacturing entails the construction of objects layer by layer based on digital 3D models as a blueprint. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods that involve cutting from a solid material block, additive manufacturing progressively builds objects by adding material layer by layer.
This approach enables the production of complex geometries with minimal material waste, making it a game-changer in different industries, including automotive, healthcare, aerospace, and consumer goods.
Types of Additive Manufacturing Processes
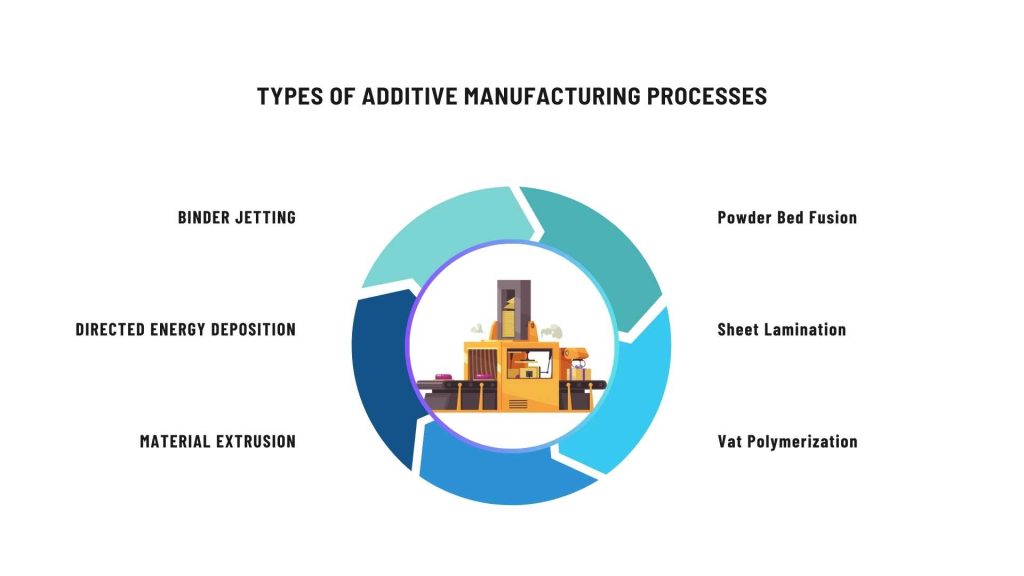
Vat Polymerization: Vat polymerization uses a photopolymer resin that solidifies when exposed to light. Selectively curing the resin material layer by layer to create the selected object.
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (Now DED-arc): This process involves the deposition of metal wire. Which is then melted using an electric arc to build up the desired shape.
Binder Jetting: This process involves jetting a binding agent onto a powder bed, layer by layer, to create the desired object.
Directed Energy Deposition (DED): It utilizes focused thermal energy to melt and fuse materials as they are deposited onto a substrate. Enabling the fabrication of large, intricate parts.
Material Extrusion: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) involves extruding molten material through a nozzle to create layers that solidify upon cooling.
Material Jetting: Material jetting, akin to conventional inkjet printing, dispenses photopolymer droplets onto a building platform. These droplets are subsequently solidified into layers through UV light exposure.
Sheet Lamination: In this method, thin sheets of material are layered and bonded together using heat, adhesive, or ultrasonic welding to create the final object.
Challenges and Considerations
Skill and Knowledge Gap:
Additive manufacturing requires specialized skills that may be limited within the existing workforce. Necessitating investments in training and development initiatives.
Data Integration and Interoperability:
Integrating additive manufacturing with existing ERP systems may require robust data integration capabilities to ensure seamless communication and interoperability between various software platforms.
Process Standardization and Compliance:
Implementing standardized processes and ensuring compliance with industry regulations pose significant challenges that need to be addressed when incorporating additive manufacturing into operations.
The Role of ERP in Manufacturing
Cloud ERP systems are pivotal in integrating additive manufacturing into existing manufacturing operations. These sophisticated software solutions facilitate seamless coordination and optimization of resources, processes. And data across various departments, enabling manufacturers to leverage the full potential of additive manufacturing technologies.
Benefits of Additive Manufacturing Integration
Enhanced Production Planning and Scheduling: Additive manufacturing allows for on-demand parts production. Reducing lead times and enabling more flexible production scheduling.
Improved Inventory Management: By transitioning to additive manufacturing. Manufacturers can reduce the need for spare parts inventories, minimizing storage costs and obsolescence risks.
Seamless Quality Control: Additive manufacturing processes can be closely monitored and controlled. Ensuring consistent quality and compliance to specifications throughout the production cycle.
Enhanced Cost Visibility and Analysis: With additive manufacturing, manufacturers can gain greater visibility into production costs. Allowing for more accurate cost analysis and informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Acumatica Cloud based ERP presents a transformative solution for Additive Manufacturing by streamlining operations, enhancing visibility, and promoting agility throughout production.
Acumatica helps additive manufacturers improve inventory management, production scheduling. And financial tracking to optimize resource allocation and respond to market demands efficiently.
By integrating robust analytics and real-time data insights, Acumatica enables businesses to make informed decisions, drive innovation. And ultimately achieve greater efficiency and competitiveness in the dynamic landscape of additive manufacturing.

Vijay comes with a vast experience in ERP and enterprise solutions space with about 20 years of experience in various packaged application like Acumatica, SAP, Orion, Salesforce.com, SugarCRM and, SalesLogix.

