A smart factory is a cyber-physical approach that utilizes cutting-edge technologies to analyze data, implement automated processes, and continuously learn from its operations.
How does a smart factory work
Automation and robotics have long been utilized in manufacturing, with traditional factories employing standalone automated machines like barcode scanners and cameras. However, these devices typically operate independently, requiring manual coordination. And integration of people, assets, and data management systems within the factory.
A smart digital factory integrates machines, people, and Big Data into a connected ecosystem. It learns from data, forecasts trends, recommends workflows and continuously improves for increased resilience, productivity, and safety.
The structure of a smart factory
The basic structure of a smart factory can be broadly summarized into three steps:
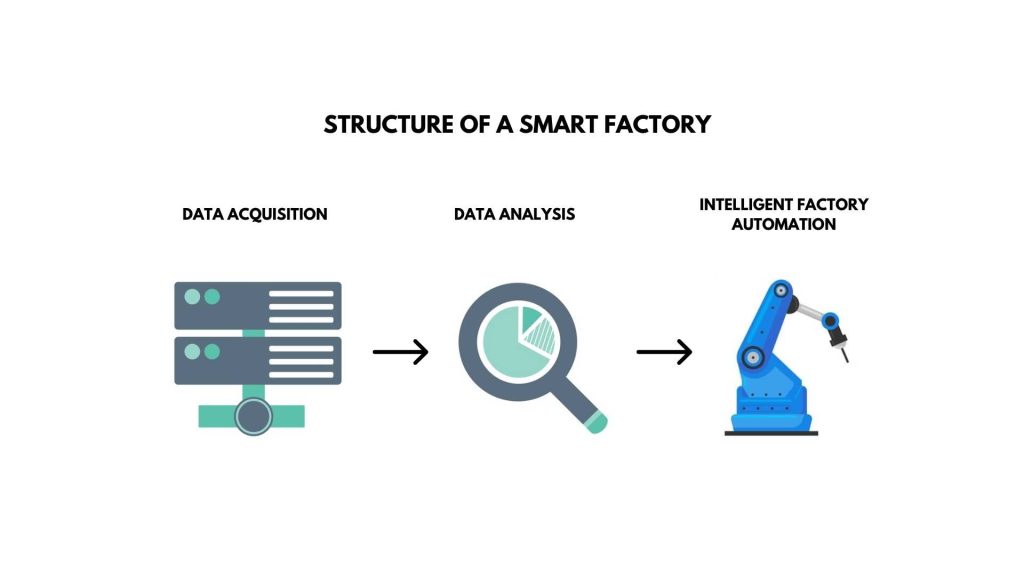
Data acquisition: Artificial intelligence and modern databases enable gathering of diverse. And valuable data from businesses, supply chains, and beyond using IoT sensors. AI systems compile data from various sources, such as performance, market trends, and logistics, for analysis.
Data analysis: Machine learning and intelligent business systems utilize advanced analytics. And data management to analyze data from IoT sensors for maintenance alerts. Market data is utilized to pinpoint opportunities, assess risks, and refine workflow efficiencies gradually. Leading to performance improvements and automatic corrections.
Intelligent factory automation: After analyzing data, workflows are established, and instructions are transmitted to machines to enable smart processes. Production priorities can be adjusted or inventory buffers utilized to prevent disruptions during demand spikes or delays.
Benefits of a smart factory
Productivity and efficiency:
Smart factory technologies aim to shift manufacturing from reactive to proactive using predictive analytics and Big Data. Benefits include optimized processes, just-in-time inventory, accurate forecasting, and increased productivity.
Sustainability and safety:
Consumers prioritize socially and environmentally responsible products, leading to increased spending. Smart factory technologies enable businesses to adopt green, safe, and socially responsible manufacturing practices.
Innovations like blockchain and RFID ensure supply chain transparency. Automation in smart factories helps reduce workplace injuries.
Product quality and customer experience:
Smart factories use cloud connectivity for real-time insights into manufacturing, improving supply chain communication and product customization. Advanced data analysis enhances competitiveness and product reviews and reduces returns/recalls.
Achieving smart factory Transformation with ERP
Data Integration: ERP systems streamline business processes across departments like production, inventory, finance, and HR, enabling unified data sharing crucial for smart factory operations.
Real-time Insights: ERP systems provide access to real-time data, enabling better decision-making and helping optimize manufacturing processes. It includes monitoring inventory levels, production status, and equipment performance.
Automation and Optimization: Cloud ERP automates workflows and optimizes production schedules through analytics. And machine learning, reducing manual effort and errors while improving efficiency.
Quality Management: ERP systems have quality management modules for monitoring product quality, tracking metrics, managing non-conformances. And implementing corrective actions to maintain consistency and standards.
Conclusion
Acumatica Cloud ERP is a transformative tool for smart factories, facilitating seamless integration, real-time data analytics, and agile decision-making. Its scalable architecture empowers manufacturers to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and adapt swiftly to market demands.
With Acumatica, smart factories can harness the power of automation and connectivity to achieve heightened efficiency. And competitiveness in the ever-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing.

Vijay comes with a vast experience in ERP and enterprise solutions space with about 20 years of experience in various packaged application like Acumatica, SAP, Orion, Salesforce.com, SugarCRM and, SalesLogix.