Effective data management is the backbone of modern food manufacturing, intricately woven into every step of the production process. From raw materials to producing the outcome of products, data is the guiding force, steering decisions, ensuring quality, and optimizing efficiency.
In this intricate dance of supply chain intricacies, harnessing, analyzing, and leveraging data isn’t just advantageous—it’s imperative. By embracing robust data management practices, food factories can also ensure the quality of their offerings, streamline operations, meet regulatory standards, and ultimately satiate the evolving appetites of today’s discerning consumers.
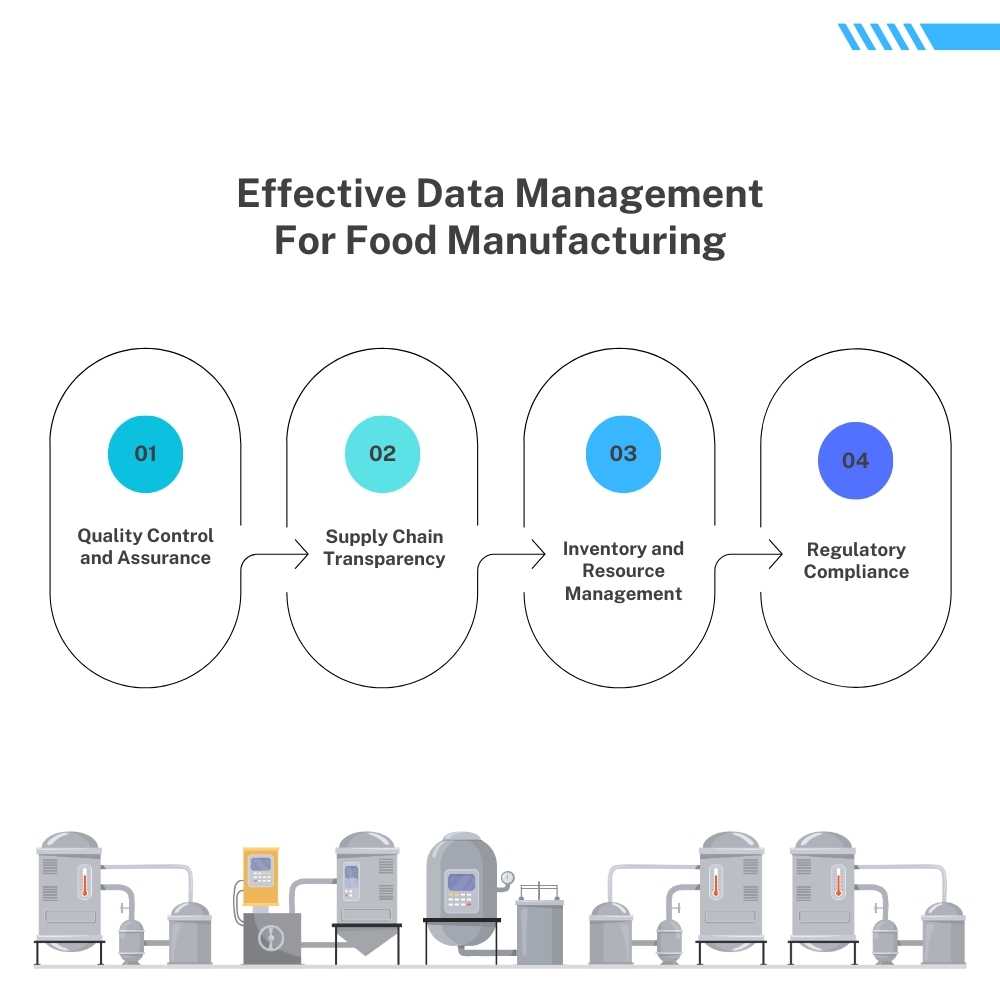
Key functionalities
Quality Control and Assurance
Data management systems are key to the quality of food products. They track and analyze diverse parameters throughout the production process, such as temperature, humidity, and ingredient sourcing, to maintain consistency and comply with stringent quality standards.
Supply Chain Transparency
Data management facilitates transparency across the supply chain. From sourcing raw materials to distribution, these systems track and trace each component’s journey, enabling manufacturers to quickly identify and address any issues like contamination or spoilage, thus ensuring the integrity of the final product.
Inventory and Resource Management
Efficient data management optimizes inventory levels by tracking stock levels, expiration dates, and usage patterns. It ensures that the right ingredients are available at the right time, minimizing waste and maximizing production efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance
Food manufacturing involves adhering to various regulations and standards. Data management systems help organize and manage compliance-related data, ensuring the company meets all necessary regulatory requirements, certifications, and audits.
trends in data management
Predictive Analytics and AI-driven Insights: With the massive influx of data from various sources along the production chain, employing predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) has become pivotal. Manufacturers leverage AI algorithms to predict equipment failures, optimize supply chain logistics, forecast consumer demand more accurately, and even enhance product quality by analyzing data patterns in real-time. Its proactive approach aids in preventing issues before they occur, optimizing resources, and ensuring consistency in the final product.
Blockchain for Traceability and Transparency: Blockchain technology is acquiring traction in the food industry due to its potential to enhance traceability and transparency. By utilizing blockchain’s immutable ledger, food manufacturers can track every phase of the supply chain, from the origin of raw materials to the distribution of the final product. This blockchain technology not only ensures the authenticity and safety of food products but also enables consumers to access detailed information about the journey of the food they consume, fostering trust and confidence in the brand.
Key challenges in data management
Quality Assurance and Compliance:
Ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and compliance with strict industry regulations (such as FDA guidelines) presents a significant challenge. Managing vast amounts of data—from ingredient sourcing to production processes—while maintaining quality standards requires robust systems and protocols.
Supply Chain Complexity:
Food manufacturing involves intricate supply chains with multiple stakeholders, suppliers, distributors, and retailers. Managing data across these networks while maintaining traceability and transparency is a considerable challenge. Issues like data silos and interoperability between different systems can hinder smooth information flow.
Data Volume and Variety:
The industry generates massive volumes of data from sensors, IoT devices, production equipment, and customer feedback. Dealing with this diverse array of data formats (structured and unstructured) and effectively leveraging it for insights poses a challenge.
Cybersecurity and Data Integrity:
Protecting sensitive data from cyber threats and ensuring its integrity throughout manufacturing is critical. With the increasing digitization of processes, the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, or tampering becomes a significant concern, demanding robust security measures.
Conclusion
Acumatica Cloud ERP is a transformative force in revolutionizing data management within the food manufacturing landscape. Acumatica empowers companies to orchestrate their data efficiently by seamlessly integrating various operations onto a unified platform. Its real-time insights enable proactive decision-making, optimizing supply chains, inventory management, and compliance with industry regulations.
ERP solutions enhance visibility across the production lifecycle and foster agility, ensuring that food manufacturers adapt swiftly to market demands while upholding the highest quality and safety standards.

Vijay comes with a vast experience in ERP and enterprise solutions space with about 20 years of experience in various packaged application like Acumatica, SAP, Orion, Salesforce.com, SugarCRM and, SalesLogix.

